Pituitary gland
PITUITARY GLAND
The pituitary gland (hypothesis) is a small gland situated at the base of the skull in the sella turcica and connected to the brain by pituitary stalk It is divided into
1. Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
2. posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis).
3. Intermediate lobe (called pars intermedia)
Hypothalamo- Hypophysial connections
Two types of connections b/w hypothalamus and pituitary gland
1- A vascular connections between hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland in the form of a hypothalamo-hypophysial portal circulation
2- A nervous connection between the hypothalamus and posterior lobe in the form of hypothalamo- hypophysial tract
....................................................................................
Anterior Pituitary Gland
It is called the “Master gland
It is essential for life
It secrete the following hormones
 ”
”
.
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
I-Polypeptide Hormones
1. Growth Hormone (GH, Somatotropin): primary hormone responsible for regulating body growth, and is important in metabolism
2. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): stimulates cortisol secretion by the adrenal cortex & promotes growth of adrenal cortex
3. Prolactin: Females: stimulates breast development and milk production. Males: involved in testicular function.
11- Glycoprotein Hormones
1. Follicle-stimulating Hormone (FSH): Females: stimulates growth & development of ovarian follicles, promotes secretion of estrogen by ovaries. Males: required for sperm production
2. Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Females: responsible for ovulation, formation of corpus luteum in the ovary, and regulation of ovarian secretion of female sex hormones.
Males: stimulates cell in the testes to secrete testosterone
3. Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH): stimulates secretion of thyroid hormone & growth of thyroid gland
GROWTH HORMONE
It is a small protein hormone (191a.a).
It causes growth of all tissues of the body including bone, muscles & viscera( except nervous tissue). It increased size of the cell & mitosis with development of large number of cells(i.e increase in tissue size; length& weight) .
It exerts its action by direct and indirect mechanism.
...................................
Cellular mechanism of action of GH (direct effect)
Activation of the
cytoplasmic
Portion of the receptors
Which has tyrosine
kinase activity that→
Stim. DNA
transcription→
formation of mRNA &
tRNA→ promote
protein synthesis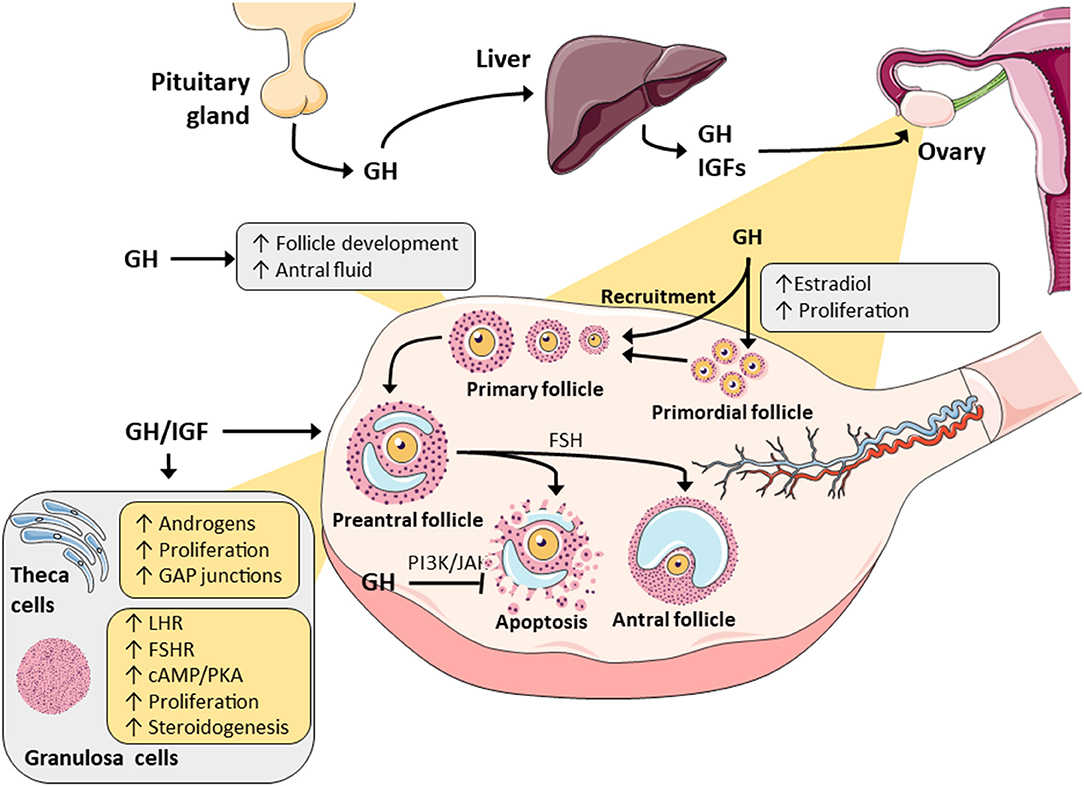
(indirect effect)

Functions of GH:-
1-Effect on growth:
GH stim growth of all tissues, It increase numbers, size & differentiation of cells.
Insulin & chat are necessary for action of growth hormone .
Somatomedin stim. epiphyseal cartilage & elongation of bone before puberty
After puberty increase bone thickness by stim. of osteoblast
II-Metabolic functions:
A) On protein: Anabolic effect
1-GH increases transport of amino acid through cell membrane to interior of the cell.
2-GH increase protein synthesis by the ribosome, .
3-GH stimulates the transcription of DNA in the nucleus causing formation of large quantities of RNA .This promotes protein synthesis & also promotes growth.
4-GH decreases catabolism of protein & amino acid (protein sparer).
B) On fat: Lipolytic effect
GH has a lipolytic effect, it increase utilization of fat leading to release of fatty acids from adipose tissue to the body fluids.
C) On carbohydrates (It is diabetogenic hormone):
1- It decreases utilization of glucose for energy; may result from the increased mobilization & utilization of fatty acids for energy.
2- It increases glycogen deposition. The glucose that does enter the cells is rapidly changed to glycogen 3- It diminishes uptake of glucose by the cells.
4-It decreases the number of insulin receptor.
III-Other functions:
1-It stimulates erythropoiesis.
2-It increases gastrointestinal absorption of calcium.
3- It decreases the rate of urinary excretion of Na+&K+ ions b/c these electrolytes are needed for the growing tissue .
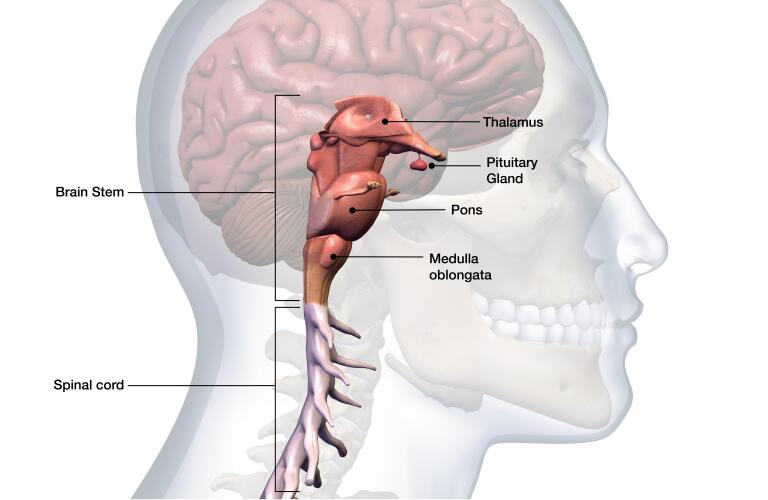
/pituitary_gland-5a0c7e374e4f7d0036270998.jpg)
To be cont...

Comments
Post a Comment