The trigeminal nerve
The Trigeminal nerve(Fifth Or Trifacial Nerve)
The trigeminal nerve is the largest cranial nerve and is the great sensory nerve of the head and face, and the motor nerve of the muscles of mastication.
|
It emerges from the side of the pons, near its upper border, by a small motor and a large sensory root.
Sensory: The three terminal branches of CN V innervate the skin, mucous membranes and sinuses of the face. Their distribution pattern is similar to the dermatome supply of spinal nerves (except there is little overlap in the supply of the divisions).
Motor: Only the mandibular branch of CN V has motor fibres. It innervates the muscles of mastication: medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid, masseter and temporalis. The mandibular nerve also supplies other 1st pharyngeal arch derivatives: anterior belly of digastric, mylohyoid, tensor veli palatini and tensor tympani.
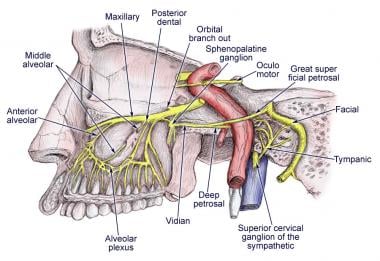
Parasympathetic Supply: The post-ganglionic neurones of parasympathetic ganglia travel with branches of the trigeminal nerve. (But note that CN V is NOT part of the cranial outflow of PNS supply)
|
Anatomical Course:
The trigeminal nerve originates from three sensory nuclei (mesencephalic, principal sensory, spinal nuclei of trigeminal nerve) and one motor nucleus (motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve) extending from the midbrain to the medulla. A nucleus (pl. nuclei) is a collection of neurone cell bodies within the central nervous system.At the level of the pons, the sensory nuclei merge to form a sensory root. The motor nucleus continues to form a motor root. These roots are analogous to the dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal cord.
In middle cranial fossa, the sensory root expands into the trigeminal ganglion. A ganglion (pl. ganglia) refers to a collection of the neurone cell bodies outside the central nervous system. The trigeminal ganglion is located lateral to the cavernous sinus, in a depression of the temporal bone. This depression is known as the trigeminal cave.
The peripheral aspect of the trigeminal ganglion gives rise to 3 divisions: ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2) and mandibular (V3).
The motor root passes inferiorly to the sensory root, along the floor of the trigeminal cave. Its fibres are only distributed to the mandibular division.
The ophthalmic nerve and maxillary nerve travel lateral to the cavernous sinus exiting the cranium via the superior orbital fissure and foramen rotundum respectively. The mandibular nerve exits via the foramen ovale entering the infra-temporal fossa. (Note – be aware that while we talk about the nerves exiting the cranial cavity, the sensory components can also be said to be entering the cranial cavity, since they are afferent fibres).
Trigeminal Nerve In The Face:
The three divisions of the trigeminal nerve; ophthalmic. maxillary & mandibular, supply the skin of most of the face.The area on the lower half of the ramus of the mandible ,close to its angle, is supplied by the great auricular nerve.

Comments
Post a Comment